How To Buy Bitcoin Cash (BCH)?

A common question you often see on social media from crypto beginners is “Where can I buy Bitcoin Cash?” Well, you’ll be happy to hear it is actually quite a simple and straightforward process. Thanks to its massive popularity, you can now buy Bitcoin Cash on most cryptocurrency exchanges, including Coinbase and Binance in 3 simple steps.
Step 1: Create an account on an exchange that supports Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
First, you will need to open an account on a cryptocurrency exchange that supports Bitcoin Cash (BCH).
We recommend the following based on functionality, reputation, security, support and fees:
1
Bybit
Fees (Maker/Taker) 0.1%*-0.1%*
Cryptocurrencies
Available for Trade 400+
Sign-up bonus
15% reduced trading fees & up to $30,000 sign-up bonus*
Available in
Europe, Asia, Oceania, Africa
2
Binance
Fees (Maker/Taker) 0.075%*-0.1%*
Cryptocurrencies
Available for Trade 500+
Sign-up bonus
10% reduced trading fees*
Available in
Europe, Asia, Oceania, Africa
In order to sign up, you will need to enter some basic information, such as your email address, password, full name and, in some cases, you might also be asked for a phone number or address.
Note: On specific exchanges, you might need to complete a Know Your Customer (KYC) procedure in order to be able to purchase cryptocurrency. This is most commonly the case with licensed and regulated exchanges.
Step 2: Deposit funds into your account
Many cryptocurrency exchanges will allow you to purchase Bitcoin Cash (BCH) with fiat currencies, such as EUR, USD, AUD and others. Furthermore, they will also provide you with multiple deposit methods through which you can fund your fiat account, such as credit and debit cards, ewallets or direct bank transfers.
Note: Some payment methods will have higher fees than others, such as credit card payments. Before funding your fiat account on your chosen exchange, make sure to do your due diligence to find out the fees involved with each payment method to avoid unnecessary costs.
Step 3: Buy Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
This process is similar across almost every cryptocurrency exchange. All you have to do is find a navigation bar or a search bar, and search for Bitcoin Cash (BCH) or Bitcoin Cash (BCH) trading pairs. Look for the section that will allow you to buy Bitcoin Cash (BCH), and enter the amount of the cryptocurrency that you want to spend for Bitcoin Cash (BCH) or the amount of fiat currency that you want to spend towards buying Bitcoin Cash (BCH). The exchange will then calculate the equivalent amount of Bitcoin Cash (BCH) based on the current market rate.
Note: Make sure to always double-check your transaction details, such as the amount of Bitcoin Cash (BCH) you will be buying as well as the total cost of the purchase before you end up confirming the transaction. Furthermore, many cryptocurrency exchanges will offer you their own proprietary software wallet where you will be storing your cryptocurrencies; however, you can create your own individual software wallet, or purchase a hardware wallet for the highest level of protection.
For more in-depth instructions, our ‘Absolute Beginner’s Guide To Cryptocurrency Investing‘ will take you through the process step-by step. In addition to providing instructions for sending and receiving your cryptocurrency.
And if you’re completely new to crypto our beginner, intermediate and advanced level articles will get you up to speed with everything you need to know about the cryptocurrency space starting out.
What is Bitcoin Cash (BCH)?
Hard forks are a potentially useful tool for launching new projects whenever politics become involved with blockchains. Bitcoin Cash (BCH) was developed by a collective of individuals who were dissatisfied with the development plans for Bitcoin. These individuals included investors, business owners, and miners. Bitcoin Cash is a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that was introduced in August of 2017 and focuses on increased scalability as well as reduced transaction fees. Bitcoin ABC is another name for the project that’s being developed (Adjustable Blocksize Cap).
Blockchain scalability
Bitcoin was plagued by slow transaction confirmation times and rising transaction fees in 2017, both of which were working against the cryptocurrency’s original promise to facilitate near-instant payments with extremely low fees. In the time leading up to the launch of Bitcoin Cash, there was a heated discussion going on within the Bitcoin community about the potential consequences of raising the maximum size of a block.
Because Bitcoin is a decentralized system, any proposed changes to the protocol require the consensus of the Bitcoin community. When making changes and updates to the Bitcoin software, it is necessary for all of the network nodes to arrive at a consensus before proceeding.
Bitcoin Cash was pitched to the public as a more scalable alternative to Bitcoin, with faster confirmation times and lower transaction fees. The Bitcoin Cash (BCH) community believes that the project is more in line with Satoshi Nakamoto’s proposal of a peer-to-peer electronic currency, and they argue that this is in line with Nakamoto’s proposal. The primary reason for this is that the alternative cryptocurrency provides a payment system that is both quicker and less expensive, making it possibly more suitable than Bitcoin for day-to-day use.
The original Bitcoin blockchain went through a long-awaited upgrade in the form of a soft fork not long after the Bitcoin Cash fork. This upgrade implemented a technology known as SegWit (Segregated Witness). Pieter Wuille, a developer working on Bitcoin, introduced an upgrade of this kind in 2015. Congestion on the Bitcoin network and other scalability issues led to the implementation of this solution on the Bitcoin network.
Before the SegWit hard fork was scheduled to occur, the SegWit soft fork was supposed to take place. However, supporters of Bitcoin Cash believed that SegWit was a subpar alternative to increasing the size limit of blocks. The Bitcoin Cash hard fork was supported by some prominent members of the blockchain industry, such as Jihan Wu, who is the co-founder of Bitmain. Roger Ver was another backer of the Bitcoin Cash fork (CEO of Bitcoin.com).
How does BCH work?
Bitcoin Cash was created by directly forking the source code of the original Bitcoin, so there are many similarities between the two. Both of these networks use a consensus mechanism known as proof of work, and they welcome participation from anyone who is interested. Additionally, any address that had Bitcoin Core (BTC) prior to the hard fork was given an equivalent amount of Bitcoin Cash (BCH) after the hard fork (same address string, but on different networks).
The target block time for BCH is the same as that of Bitcoin, which is 10 minutes, and the maximum supply of BCH coins is 21 million. Every 210,000 blocks, the rate of BCH emissions drops by one-half (roughly every four years). The current value of the block reward is 6.25 BCH for each individual block.
Bitcoin Cash, in contrast to Bitcoin, has an increased limit on the size of each block, which enables a greater number of transactions to be included in each block. The maximum size of a block could be increased from 1 MB to 8 MB in the beginning, and then it was increased to 32 MB in 2018.
In actual use, however, the average size of a Bitcoin Cash block has only crossed the 1 megabyte threshold a few times since 2017. On the website BitInfoCharts.com, there is a comparison that shows the difference between the average block size of BTC and BCH.
The so-called difficulty adjustment algorithm is used to make adjustments to the amount of computational effort required for mining Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash (DAA). However, the mining difficulty of Bitcoin Cash is adjusted after each block, whereas Bitcoin only adjusts itself once every 2016 blocks.
In the past, Bitcoin Cash made use of an algorithm known as emergency difficulty adjustment (EDA), which aimed to lessen the difficulty of mining and provide miners with an incentive to join the Bitcoin Cash network. However, after some time, the algorithm was taken out of use because it was unstable. One of the reasons why the Bitcoin Cash blockchain is thousands of blocks ahead of the Bitcoin blockchain is because of the implementation of EDA.
Schnorr Signatures is a new technology that was introduced into Bitcoin Cash in 2019, and it is an alternative algorithm that modifies the way digital signatures are utilized. Compared to the ECDSA scheme, which is currently in use by Bitcoin, the Schnorr Signatures scheme is not only straightforward and safe, but it also enables greater levels of privacy and scalability.
BCH key features
- The BCH source code was based on the original Bitcoin protocol.
- The supply is capped at 21 million.
- As a fork of Bitcoin, BCH also uses the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to issue new coins.
- Increased block size from 1 MB to 32 MB.
- The community argues that the BCH ethos aligns more closely with Satoshi’s original plans.
- The BCH mining difficulty is adjusted after each block through the difficulty adjustment algorithm (DAA).
- BCH did not implement SegWit.
- BCH implemented Schnorr Signatures in 2019.
- Smart contract development built-in as a later update.
What makes Bitcoin Cash (BCH) unique?
Bitcoin Cash is a decentralized peer-to-peer electronic cash system that does not rely on any central authority like a government or financial institution. As such, it represents a fundamental redesign of the very nature of money. The core features of Bitcoin Cash are:
- Open to anyone. Nobody controls or owns Bitcoin Cash. There’s no CEO, and you don’t need to ask for permission to use it.
- Pseudonymous. Identities are not tied to transactions. This helps to ensure that Bitcoin Cash remains free to be used by anyone, without censorship.
- Transparent. All transactions are recorded on a global public ledger called the blockchain. The ledger is updated at regular intervals in blocks that are connected to form a chain. This allows anyone to easily see the full history of ownership, and helps to eliminate the potential for fraud.
- Distributed. The public ledger (blockchain) is stored voluntarily by a network of participants known as ‘nodes.’ This helps to ensure the longevity of information.
- Rules-based. Nodes follow a set of rules (a protocol) to achieve consensus on the state of the ledger. This consensus is what constitutes the ‘truth’ as to who owns what. The protocol, however, can evolve as participants demand – although there is high-degree of consensus required to make changes. This makes Bitcoin Cash a quasi-political system, with participants forming a kind of social contract.
- Immutable. The technology deployed means that, once recorded in the blockchain, transactions effectively cannot be altered.
- Secure. Through a process known as Proof of Work (PoW), ‘miners’ compete to add new blocks to the chain that constitutes the ledger (again, the blockchain). The hardware and energy costs associated with PoW mining contribute to the security of the network along game-theory driven principles such that attacking the network is both prohibitively expensive and guarantees the attacker cannot profit directly.
- Fixed supply. Only 21 million coins will ever be created. This makes Bitcoin Cash a hard asset, like land or gold, providing an opportunity for people to store value in digital realm over long periods of time.
- Low Fees. Bitcoin Cash enables reliable, fast, and affordable transactions of any value and regardless of location (including cross-border transactions). This makes it an effective alternative to payment networks like Visa and Mastercard.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) as a medium of exchange
Bitcoin Cash makes it possible for users to send and receive payments directly with one another, much like cash but on the blockchain. Transaction fees for sending Bitcoin Cash are typically less than one penny, and settlement takes place nearly instantly, regardless of where participants are located physically. Because of this, Bitcoin Cash can be useful not only for international trade and money transfers, but also for transactions as commonplace as the purchase of groceries. Bitcoin Cash is useful for use cases involving microtransactions like tipping content creators and rewarding app users because the fees and transaction times are so much lower than those associated with Bitcoin.
What’s the difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash?
Since its split in 2017, multiple independent teams of developers working on the Bitcoin Cash protocol have introduced a number of innovations with the goal of enhancing Bitcoin Cash’s usability as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that promotes economic liberty. The following is a rundown of the key developments that distinguish Bitcoin Cash from its predecessor, Bitcoin.
Maximum block size
Bitcoin Cash has a larger maximum block size (32MB) than Bitcoin (1MB). The greater number of transactions that can be processed by the Bitcoin Cash network on chain is a direct result of the increased block size. Bitcoin can process between 3 and 7 transactions per second on average, but Bitcoin Cash has the potential to process up to 200 transactions per second. This helps to reduce the cost of each transaction while also increasing the speed of transactions and the reliability of transactions. The fees associated with Bitcoin Cash transactions are typically less than one penny. In comparison, the median transaction fee for Bitcoin (BTC) has been in the range of $1-15 since the year 2020.
Smart contract support
Bitcoin Cash developers can use smart contract languages like Cashscript to enable more complex functions than the basic transactions that are possible on Bitcoin. This creates the possibility of ‘decentralized finance’ applications like synthetic derivates trading. Other use cases include private payments with tools such as CashShuffle and CashFusion. It also allows for ‘token issuance’ (see below).
Token issuance
Developers have the ability, through the use of the Simple Ledger Protocol, to issue new tokens that will exist on the Bitcoin Cash blockchain in a manner that is analogous to how ERC-20 tokens exist on the Ethereum blockchain. For instance, Tether, the most prominent provider of US Dollar-pegged stablecoins, has issued USDT tokens that can be found on the Bitcoin Cash chain. Because of this, individuals can use a digital wallet that does not involve a custodian to send and receive USDT for a very low cost per transaction.
Non-Fungible Tokens
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are supported by the Simple Ledger Protocol as well, and their functionality is analogous to that of Ethereum’s ERC-721 standard. The fact that NFTs are digital tokens that can be differentiated from one another is the defining characteristic of this type of asset. This enables a wide variety of potential use cases, ranging from marketplaces for digital artwork to items that can be traded within games.
Schnorr signatures
This is a digital signature scheme that enables signing capabilities that are more complex. Transactions that use Schnorr signatures take up less space, so the costs associated with those transactions are lower. Despite the fact that Schnorr signatures are currently being supported by the Bitcoin Cash protocol, there has not been a widespread adoption of them by wallet providers. When widespread adoption of Schnorr signatures occurs, there is a possibility that this will improve the fungibility of tokens, leading to an increase in the level of privacy provided by the network (effectively making all transactions appear to third-party observers to be more similar to each other).
Difficulty adjustment algorithm
Bitcoin Cash uses an algorithm referred to as aserti3-2d that makes use of an exponential moving target difficulty adjustment. If a block is more than two days late with its completion, the difficulty of the task is cut in half; however, if it is completed two days early, the difficulty of the task is increased by a factor of two. Even if there is a lot of price volatility and hash power elasticity, this difficulty adjustment algorithm helps to make sure that new blocks are generated at a consistent rate (every 10 minutes). For instance, in the event that SHA256 miners move their hashing power from BTC to BCH and back again, the difficulty adjustment algorithm underlying Bitcoin Cash will ensure that blocks continue to be produced at the desired consistent rate.
Bitcoin Cash development updates in 2023
In 2023, Bitcoin Cash (BCH) has experienced a range of significant developments, enhancing its functionality and appeal in the cryptocurrency space. Here’s an overview of the most crucial updates:
Introduction of CashTokens: A major upgrade occurred on May 15th, enabling the creation of tokens with the same properties as BCH, known as “CashTokens”. This upgrade allows developers to create a variety of applications, from payment stablecoins to event tickets, and even decentralized exchanges (DEXs), security vaults, and bridged sidechains. Despite initial excitement and a temporary surge in BCH’s price, the upgrade also brought challenges, such as increased fees and a backlog of transactions.
Locking-In Cash Improvement Proposals (CHIPs): BCH’s upgrade process in 2023 included locking in several CHIPs by November 15th for activation on ‘chipnet’. These proposals needed to demonstrate widespread approval from various stakeholders in the Bitcoin Cash ecosystem, including service providers, exchanges, businesses, miners, and development teams. Notable CHIPs included proposals to restrict transaction versions, allow smaller transaction sizes, and introduce CashTokens and Pay-to-Script-Hash (P2SH) outputs for stronger contract security.
Integration with Gaming and Betting Platforms: BCH has been increasingly adopted by gaming hubs and online casinos as a payment method. This integration provides a range of gaming options for users, from slots and table games to poker and sports betting, leveraging BCH’s quick transaction confirmations and lower fees compared to other cryptocurrencies. This widespread adoption in online gaming reflects BCH’s growing influence in the digital economy.
Ongoing Market Performance and Potential Future Developments: Bitcoin Cash has shown resilience and growth in the market, particularly in e-commerce and online gaming. Looking ahead, BCH is expected to focus on improving scalability to handle more transactions per second and potentially integrate further with DeFi platforms. As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, it will be important to monitor how BCH adapts to changing market conditions and regulatory environments.
These updates and developments indicate that Bitcoin Cash is actively evolving, focusing on increasing its utility, scalability, and market adoption, which could significantly impact its role and value in the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Official website: https://bch.info/en/
Best cryptocurrency wallet for Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
There are plenty of different crypto wallets available. The best one for you depends on your general trading habits and which provides the most security in your situation. There are two main types of wallets: hot storage wallets (digital) and cold storage or hardware wallets (physical). Both have their pros and cons, and there is not necessarily a right or wrong answer when it comes to figuring out which crypto wallet is best for you.
HOW DO I DECIDE WHICH cryptocurrency WALLET TO USE for Bitcoin Cash (BCH)?
Deciding which type of wallet to use depends on a variety of factors, including:
- How often you trade. In general, hot wallets are better for more active cryptocurrency traders. Quick login ability means you are only a few clicks and taps away from buying and selling crypto. Cold wallets are better suited for those looking to make less frequent trades.
- What you want to trade. As mentioned earlier, not all wallets support all types of cryptocurrencies. However, some of the best crypto wallets have the power to trade hundreds of different currencies, providing more of a one-size-fits-all experience.
- Your peace of mind. For those worried about hacking, having a physical cold wallet stored in a safe deposit box at the bank or somewhere at home, provides the safest, most secure option. Others might be confident in their ability to keep their hot wallets secure.
- How much it costs. It is important to investigate the costs associated with each wallet. Many hot wallets will be free to set up. Meanwhile, cold wallets, like any piece of hardware, will cost money to purchase.
- What it can do. While the basics of each cryptocurrency wallet are the same, additional features can help set them apart. This is especially true of hot wallets, many of which come with advanced reporting features, insights into the crypto market, the ability to convert cryptocurrencies and more. Security features can also be a good differentiator.
For a more in-depth overview of cryptocurrency wallets visit our “Cryptocurrency Wallets Explained” guide.
If you’re going to be dealing in larger volumes of crypto, investing in cold storage might prove advantageous.
Most widespead examples of this being the Ledger Nano and the Trezor.
Ledger manufactures cold storage wallets designed for users who want increased security. Their wallets are a physical device that connects to your computer. Only when the device is connected can you send your cryptocurrency from it. Ledger offers a variety of products, such as the Ledger Nano S and the Ledger Nano X (a bluetooth connected hardware wallet).
Trezor is a pioneering hardware wallet company. The combination of world-class security with an intuitive interface and compatibility with other desktop wallets, makes it ideal for beginners and experts alike. The company has gained a lot of the Bitcoin community’s respect over the years. Trezor offers two main models – The Trezor One and Trezor Model T (which has a built in touch screen).
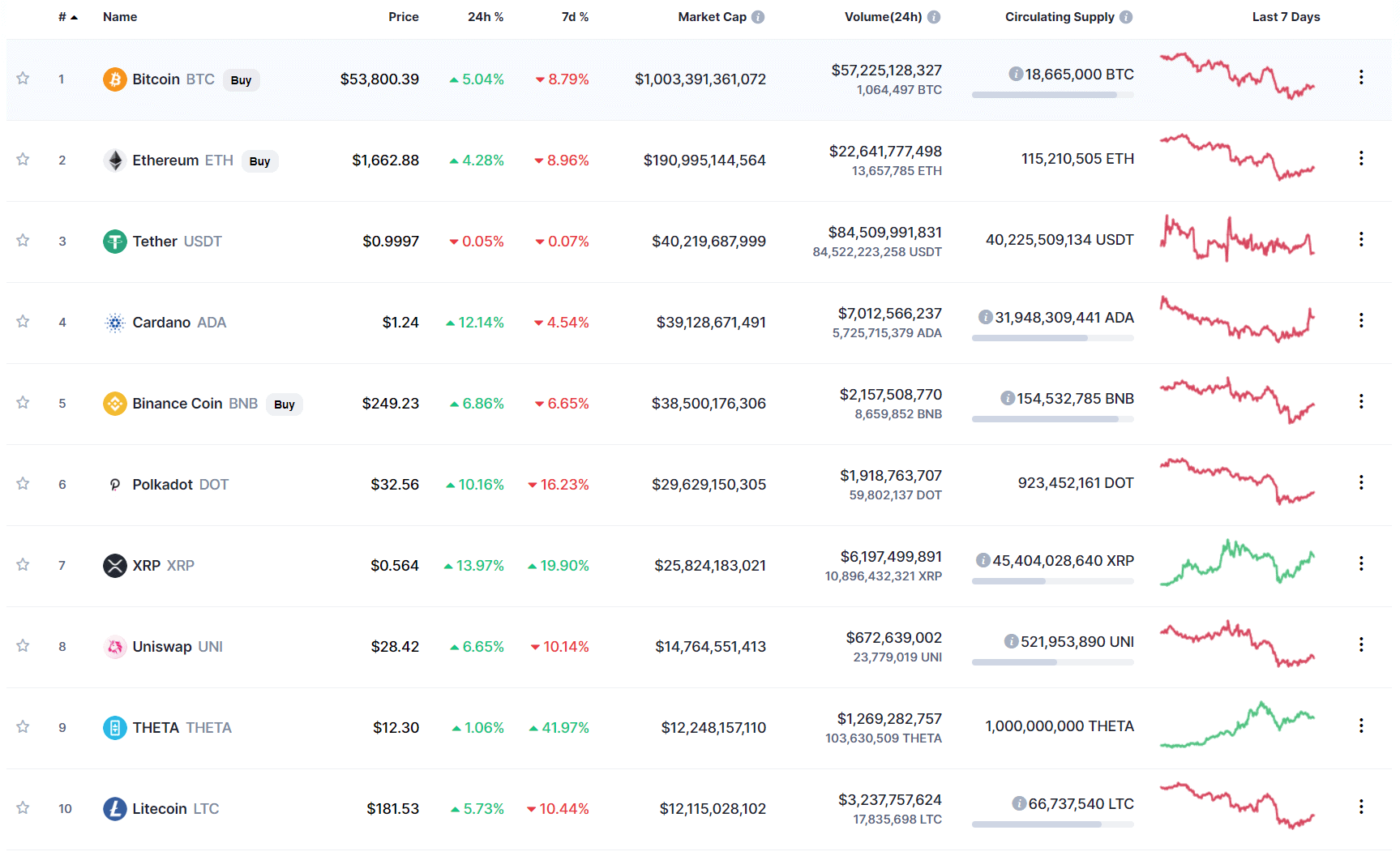
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) Price & Charts
- Market Capitalization And Daily Trading Volume
- Current Market Price Of Every Cryptocurrency Relative To USD (And Some Local Currencies)
- Circulating And Total Supply
- Historical Charts With Prices Relative To USD, Bitcoin (BTC), And Ethereum (ETH).