What Is A Stablecoin?
What is a stablecoin?
Stablecoins are a kind of digital asset that are supposed to have a value that is comparable to that of fiat currencies such as the dollar or the euro. They make it possible for users to move wealth over the world in a quick and inexpensive manner while preserving the value of the currency.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are two examples of cryptocurrencies that are known for their extreme price volatility when compared to traditional currencies. Due to the fact that blockchain technology is still in its infancy and cryptocurrency marketplaces are still relatively undeveloped, this is to be anticipated. When it comes to usability, the fact that the value of a cryptocurrency isn’t tied to any particular item is intriguing from the point of view of the free market, but it may make using cryptocurrencies more difficult.
The use of cryptocurrencies as means of trade may be said to benefit greatly from their underlying blockchain technology. However, due to the volatility of their values, they have finally become assets that carry a significant level of risk and are not a good choice for making payments. When a transaction is finalized, the value of the coins that were delivered may be much higher or lower than it was when the transaction was initiated.
However, stablecoins do not face this challenge. These assets see almost little price volatility and closely follow the value of the asset or currency that they replicate, whether that be a fiat currency or an underlying asset. Because of this, they are dependable assets that may be used as safe havens when the market is turbulent.
There are a few different strategies that may be used so that a stablecoin can keep its stability. In this post, we will talk about some of the techniques that are employed, as well as the benefits and drawbacks of using them.
How do stablecoins work?
There are a few different categories of stablecoins, and each of them approaches the process of pegging its units in a different manner. The following is a list of some of the most often used varieties of stablecoin.
Fiat-backed stablecoins
The kind of stable coin that is directly backed by fiat money with a 1:1 ratio is by far the most common and hence also the most popular. These stablecoins are also known by the name fiat-collateralized stablecoins. A central issuer, often known as a bank, is responsible for maintaining a reserve of fiat money and distributing tokens in accordance to that reserve.
For instance, the issuer may have one million dollars in their possession and give out one million tokens, each of which is worth one dollar. Users are able to do with these what they would do with tokens or cryptocurrencies, which is freely exchange them, and holders are able to do with them what they would do with their USD equivalent at any moment.
It is very clear that there is a significant amount of counterparty risk there, which cannot be reduced; ultimately, the issuer has to be trusted. A user cannot ascertain with any degree of certainty if the issuer maintains cash in reserve since there is no means to do so. The issuing corporation may, at most, make an effort to be as open and transparent as possible with regard to the publication of audits, but the system is by no means untrustworthy.
Binance provides a pair of stablecoins that are backed by fiat currency: BUSD and BGBP. BUSD is pegged to the US dollar, while BGBP is linked to the value of the British pound.
Crypto-backed stablecoins
The primary distinction between crypto-backed stablecoins and their fiat-backed equivalents is the kind of asset that is utilized as collateral. In this case, the asset in question is cryptocurrency. However, given the digital nature of bitcoin, the distribution of units is managed via smart contracts.
Despite the fact that confidence in crypto-backed stablecoins is diminished, it is important to highlight that voters are the ones who decide monetary policy as part of the governance systems of cryptocurrencies. This indicates that you are not placing your faith in a single issuer, but rather you are placing your trust in the fact that all players in the network will always behave in the best interests of the users.
Users are required to lock their cryptocurrency into a contract before receiving the stablecoin token in order to complete the acquisition of this kind of stablecoin. After some time has passed, in order to retrieve their initial collateral, they pay stablecoins back into the original contract (along with any interest).
The precise techniques that are used to enforce the peg differ from one system to another because to the different architecture of each system. It is sufficient to argue that a combination of game theory and on-chain algorithms provide players with an incentive to maintain the price stability.
Algorithmic stablecoins
If the price of the stablecoin falls below the price of the fiat currency that it monitors, an algorithmic stablecoin system will lower the amount of tokens available for purchase. If the price rises above the value of the underlying fiat currency, then the number of circulating stablecoins will be increased to compensate for the loss in value.
You could also come across the term “non-collateralized stablecoins” while discussing this kind of tokens. This is technically inaccurate since they are collateralized, but not in the same sense as the previous two entries. However, this is still considered to constitute collateralization. In the event that a black swan occurs, algorithmic stablecoins may include some form of collateral pool to deal with the very erratic market fluctuations.
Stablecoins use cases
Stablecoins that are backed by collateral are by far the most popular kind used in practice. Some examples of these currencies include the USD Tether (USDT) cryptocurrency, the True USD (TUSD) cryptocurrency, the Paxos Standard (PAX) cryptocurrency, the USD Coin (USDC) cryptocurrency, and the Binance USD cryptocurrency (BUSD). However, there are also examples of the aforementioned other two categories that may be found in the products that are now accessible on the market. Bitshares USD and DAI are two instances of crypto-collateralized currencies, whilst Carbon and Basis (which is no longer in circulation) are examples of algorithmic versions.
This list is far from exhaustive. The emergence of hundreds of new stablecoin initiatives is proof of the significant demand for digital currencies that can be relied upon to maintain their value.
BUSD vs USDT
Paxos and Binance collaborated to create the stable cryptocurrency known as BUSD. Paxos is the issuer of many stablecoins, including the Paxos Standard (PAX) token, the HUSD coin, and the PAX Gold coin (PAXG).
BUSD are authorized and controlled by the New York State Department of Financial Services, and it is 100% backed by U.S. dollars stored in FDIC-insured U.S. institutions. BUSD are issued by the New York State Department of Financial Services. Additionally, a third-party auditing company known as Withum conducts monthly audits of BUSD to determine whether or not the money stored in banks corresponds to the supply of BUSD, which may be seen here. On the other side, USDT transactions are not subject to regular audits. The results of Tether’s most recent audit, which were conducted by Sporkin & Sullivan LLP and published on the company’s website, date back to 2018. On the other hand, they do update their public website each day with the current value of their reserves, which may be seen here.
One other distinction that can be made between BUSD and USDT is that the reserve that supports USDT is kept in offshore institutions, which are known for having a lower level of credibility. To this day, there have also been a lot of claims made concerning Tether, and you can see a summary of them here.
Therefore, one may claim that BUSD is a more secure currency than USDT. This is an accurate statement. However, if you are a typical trader, it will not make much of a difference to you whether you trade the BTC/BUSD pair or the BTC/USDT pair.
But if you want to keep particularly big quantities of money in the form of stablecoins, it could be a better option to retain simply BUSD or to divide the money between BUSD and USDT. Trading coin-margined futures rather than USDT-margined futures on Binance or other exchanges may also be a safer option in the event that a catastrophic event relating to Tether occurs.
Aside from that, there is not really any other distinction between BUSD and USDT at all. If you are a typical trader, you should focus more on looking for volume, arbitrage possibilities, and other such things.
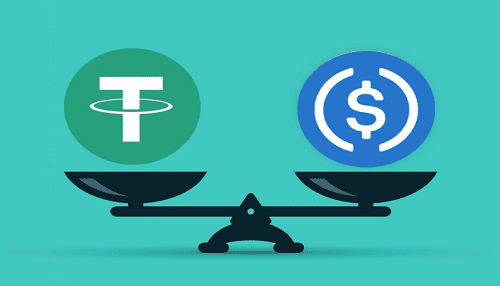
USDC vs USDT
Following in the footsteps of USDT as the biggest stablecoin by market cap is USD Coin (USDC). Circle and Coinbase are two of the original members of the Center, the membership-based consortium that governs USDC and other digital currencies.
So USDC is basically a stablecoin launched and governed by Circle and Coinbase. Just with BUSD, USDC undergoes monthly audits conducted by an independent accounting company known as Grant Thornton LLP. In contrast to Tether, the business behind USDC complies with legislation in the United States and collaborates with well-established financial institutions and auditors (USDT). So USDC, just like BUSD, is safer and more transparent than USDT.
If we look at USDC and BUSD side by side, we can see that both stablecoins are really rather comparable to one another since they both adhere to the rules of the United States and collaborate with banks and auditors based in the United States.
To reiterate, if you are a trader, you have the ability to trade pairings involving either USDC or USDT. It does not actually make that much of a difference. However, if you want to open substantial positions on cryptocurrencies, you should choose coin-margined goods rather than USDT-margined ones as your preferred choice for margined products. To further reduce the risk, you may hedge your bets by holding many stablecoins rather than relying on just one.
Stablecoins pros and cons
The possibility of stablecoins to serve as a complementary medium of exchange to cryptocurrencies is the primary benefit associated with the use of these digital assets. Because of the high levels of volatility they experience, cryptocurrencies have not been able to reach broad adoption in applications that are used in daily life such as the processing of payments. These currencies that have been stabilized provide greater degrees of predictability and stability, which allows for the issue to be solved once and for all.
Stablecoins might potentially play a role in the integration of cryptocurrencies with conventional financial markets by serving as a hedge against price fluctuations. The current state of affairs sees these two markets functioning almost entirely independently from one another, creating two distinct ecosystems. It is highly probable that cryptocurrencies will see growing use in loan and credit markets that, up to this point, have been controlled entirely by government-issued fiat currencies. This is extremely likely since a more stable form of digital money will soon be accessible.
Stablecoins may be used by traders and investors as a means of hedging their portfolios, in addition to the fact that they are beneficial in the context of financial transactions.
Stabilized coins may be an effective strategy to lower overall risk, which can be accomplished by allocating a particular amount of a portfolio to them. On the other hand, keeping a value store that can be utilized to acquire other cryptocurrencies when their prices decline might be a useful approach. In the same vein, one does not need to sell these coins in order to “lock in” profits achieved on price increases since there is no need to sell them.
Stablecoins still have several obstacles to overcome, despite the fact that they have the potential to assist in the mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies. Because a centralized institution is required in order to keep the supporting assets, fiat-collateralized variations of cryptocurrencies are not as decentralized as standard cryptocurrencies. When it comes to crypto-collateralized and uncollateralized currencies, users are required to put their faith in the larger community (as well as the source code) in order to assure the sustainability of the systems. Because these are relatively new technologies, it will take some time for them to reach their full potential.
Conclusion
Stablecoins are an essential component of the cryptocurrency markets, despite the fact that they do come with a few drawbacks. These digital currencies, which use a variety of techniques, have the potential to maintain prices that are more or less constant. Because of this, they can be used dependably not just as means of exchange but also as safe havens for traders and investors to store their money in.
Stablecoins were first conceived as a means of providing traders with an efficient instrument to control risk; nevertheless, it is now abundantly evident that their uses extend well beyond trading. They are a strong instrument that might boost the cryptocurrency ecosystem as a whole, serving in use cases where volatile alternatives are not appropriate. This could be accomplished by acting as a middle ground between fiat money and cryptocurrencies.